Introducing MindsDB Playground: Your all-in-one MindsDB Companion App
A comprehensive guide about the making, features and usage of the App.
Introduction
Machine Learning has become the need of the hour as the technologies widely depend on leveraging data to gain insights and make precise decisions. But developing and utilizing machine learning models is a tough task that is quite time-consuming and requires expertise in programming, algorithms and data analysis. So, it has become necessary now to reduce these underlying efforts and utilize the power of AutoML in abundance.
In such a case, MindsDB serves as a revolutionizing tool in the world of AutoML. MindsDB is an open-source, automated machine learning (AutoML) framework that works as an AI layer on top of your existing databases and allows you to build, train, and deploy predictive models without writing any code. It uses its underlying candidate models that are robust and precise and can easily identify the most relevant features in a dataset to accurately predict the target values.
MindsDB Playground is a web application with a simple and user-friendly interface that can be used by users to interact with different applications powered by MindsDB. The application is built using the Node Express platform and the UI is powered by HTML, CSS and JavaScript. This website lists tons of apps under NLP ( Natural Language Processing) and Prediction Model (Classification, Regression and Timeseries) categories for the users to try out the effectiveness of MindsDB in real-world scenarios.
This blog post will provide a comprehensive guide to the MindsDB Playground, discussing its features, applications, and how to use it.
Application Flow
The flow of the application begins when a user browses the application in a web browser. The user can then submit a request to the server, which is then processed by the server-side code to generate the appropriate response. The response or the error, if any, is then sent back to the client side and is displayed to the user in the web browser.
Now let us briefly understand how the client-side and server-side functions interact with each other to retrieve the desired result.
Client-Side
The client-side code collects the user input, sends a request to the server, and finally displays the result to the user.
When the webpage loads, the user can choose to interact with the application they want. They have to simply pass the input in textarea and then submit the form on the webpage. This invokes the handleFunction method. This function first prevents the default form submission behaviour, which would cause the page to refresh. It then retrieves the user input from the input textarea and clears it out on the webpage for the next run.
You can find a snippet of the HTML form that is used on the webpage below.
<form class="home-form" onsubmit="handleFunction(event)">
<textarea
id="functionInput"
required="true"
placeholder="Paragraph Here"
class="home-textarea textarea"
></textarea>
<div class="home-radio-buttons">
<h1 class="home-text17">Select Engine:</h1>
<input
type="radio"
id="functionOpenAI"
name="functionEngine"
value="OpenAI"
required=""
title="OpenAI"
class="home-open-a-radio"
/>
<label class="home-open-a-label">OpenAI</label>
<input
type="radio"
id="functionHuggingFace"
name="functionEngine"
value="HuggingFace"
required=""
title="HuggingFace"
class="home-hugging-face-radio"
/>
<label class="home-hugging-face-label">Hugging Face</label>
</div>
<button id="findFucntion" type="submit" class="home-view02 button">
Execute Function
</button>
</form>
<!-- Result Div Below -->
<div class="home-result morph" id="functionDiv">
<button class="home-button02 button" title="Close">
<svg viewBox="0 0 1024 1024" class="home-icon22">
<path
d="M810 274l-238 238 238 238-60 60-238-238-238 238-60-60 238-238-238-238 60-60 238 238 238-238z"
></path>
</svg>
</button>
<p class="home-text18" id="functionResult"></p>
</div>
The client-side code also displays a loading screen while processing this request to keep the user informed. This is simply achieved by setting the display style property of the loading-screen element to block.
The client-side code makes a POST request to the server's /findFunctionResult endpoint with a JSON payload that contains the user input and any other required details such as the selectedEngine . The fetch API is used to make this request with the appropriate headers and body.
Find the snippet for the handleFunction() method below as an example.
function handleFunction(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const query= document.getElementById("fucntionInput").value;
const resultDiv = document.getElementById("functionResult");
// Clear the input field
document.getElementById("fucntionInput").value = "";
// Loading Screen
document.getElementById("loading-screen").style.display = "block";
const engines = document.getElementsByName("functionEngine");
const selectedEngine = Array.from(engines).find(
(engine) => engine.checked
)?.value;
const functionCloseButton = document.querySelector(".home-button02");
const functionDiv = document.querySelector("#fucntionDiv");
functionCloseButton.addEventListener("click", () => {
functionDiv.style.display = "none";
});
// Send a POST request to /findFunctionResult endpoint
try {
fetch("/findFunctionResult", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
},
body: JSON.stringify({ query, selectedEngine }),
})
...continued
The server then responds with a JSON payload containing either the desired result or any error that occurred. The client-side code analyzes the response and checks for errors, if any. In case there is no error, it displays the result to the user by setting the innerHTML property of the functionResult element with a formatted string of the result. The loading-screen is not visible anymore as its display property is set to none now and instead, the functionDiv is displayed containing the result.
Here is the ...continued code from the above snippet that sets the result back to the user.
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
// Display the prediction
if (!data.error) {
resultDiv.innerHTML =
"The result is: <br/><br/>" +
data.result +
"<br/><br/> Powered by " +
data.selectedEngine;
document.getElementById("loading-screen").style.display = "none";
document.getElementById("functionDiv").style.display = "block";
} else {
resultDiv.innerHTML =
"We are caught in the middle of an error. Please try Again!";
document.getElementById("loading-screen").style.display = "none";
document.getElementById("functionDiv").style.display = "block";
}
})
.catch((error) => {
document.getElementById("loading-screen").style.display = "none";
alert("An error occurred while summarizing the text");
throw error; // Throwing the error
});
} catch (error) {
document.getElementById("loading-screen").style.display = "none";
alert("An error occurred while summarizing the text");
}
}
In case of an error during the process, the error message is set in the functionResult element and is shown to the user instead of the result after hiding the loading-screen .
There is also a Close button in the functionDiv element. The client-side code attaches an event listener to it so that the users can close this element after viewing the result.
Server-Side
The server side handles the analysis or prediction/forecasts based on engines like OpenAI or HuggingFace or the historical data. The server provides an HTTP endpoint /findFunctionResult that accepts a POST request containing a JSON payload with the user input. It then uses this input to query the respective underlying model and returns a JSON response. In case of an error, it returns an error message instead of the result.
Here is a snippet of the /findFunctionResult endpoint from the server-side app.js file.
app.post("/findFunctionResult", async (req, res) => {
const inputText = req.body.inputText;
const selectedEngine = req.body.selectedEngine;
try {
// Call the function from mindsdb.js
const result = await mindsdb.executeMindsDBQuery(query, selectedEngine);
res.send({ result, selectedEngine });
} catch (error) {
logger.error("Error extracting result: ", error);
res
.status(500)
.send({ error: "An error occurred while extracting result." });
}
});
Applications
The MindsDB Playground includes several applications that use OpenAI or HuggingFace or LightWood engine to perform automated data analysis or predictions. We will be discussing each of these applications below in detail.
NLP Models
The MindsDB Playground App features eight NLP applications that are powered by either the OpenAI engine or the HuggingFace Engine. Let's discuss each of them one by one below.
Behind the scenes, there's a handler function on the server side that interacts with the MindsDB Cloud, executes the required query and then returns the result. Find the snippet of the code below.
async function executeMindsDBQuery(query, selectedEngine) {
let retries = 3;
const retryDelay = 1000;
let modelName;
if (selectedEngine === "OpenAI") {
modelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_MODEL_NAME;
} else if (selectedEngine === "HuggingFace") {
modelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_MODEL_NAME;
}
while (retries > 0) { //Retries upto 3 times in case of an error
try {
const escapedQuery = query.replace(/"/g, ""); // Escape double quotes
const text = `SELECT responseColumn FROM ${modelName} WHERE label="${escapedQuery}"`; // SQL query statement to be executed
const response = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
if (!response.rows) {
throw new Error("Invalid response from MindsDB");
}
return response.rows; //Returns the response
} catch (error) {
logger.error(`Error executing query: ${query}`, error);
retries--;
if (retries === 0) {
throw new Error("Maximum number of retries reached");
}
await new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, retryDelay)); // Waits for 1 second before retrying
}
}
}
Some important parameters to note here are as follows:
query: It contains the user input text.escapedQuery: We escape any double quotes present in the input text so that SQL can parse it easily without any errors.modelName: It is selected based on the user selection retrieved from theselectedEngineparameter.text: It contains theSELECTstatement that needs to be executed.retries: The function is designed to retry 3 times in case of an error to make the functionality somewhat fail-safe.retryDelay: The duration between each retry in case of a failure, which is set to 1 second by default.
The first 4 parameters will change as per the user input and the specific application that they are trying to run.
Text Summarization
The Text Summarization application allows users to summarize long texts into shorter versions. Users can input a long text into the app, select the NLP engine of their choice (OpenAI or HuggingFace), and get a summarized version of the text.

The 4 parameters for the Summarize Text App will be as follows.
if (selectedEngine === "OpenAI") {
summaryModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_SUMMARY_MODEL_NAME;
} else if (selectedEngine === "HuggingFace") {
summaryModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_SUMMARY_MODEL_NAME;
}
const escapedMessage = summary.replace(/"/g, "");
const text = `SELECT summary FROM ${summaryModelName} WHERE text="${escapedMessage}"`;
const summaryResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can provide a summary of the input texts.
For the OpenAI engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
Create Model openai_article_summarizer
PREDICT summary
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
min_tokens = 45,
max_tokens = 200,
prompt_template = 'Provide a short and informative
summary of the following text. text:{{text}}';
For the HuggingFace engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL hf_article_summarizer
PREDICT summary
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'summarization',
model_name = 'sshleifer/distilbart-cnn-12-6',
input_column = 'text',
min_output_length = 10,
max_output_length = 200;
Sentiment Analysis
The Sentiment Analysis application allows users to analyze the sentiment of a text. Users can input text into the textarea in the app, select the NLP engine of their choice (OpenAI or HuggingFace), and get the sentiment of the text i.e., Positive, Negative, or Neutral.
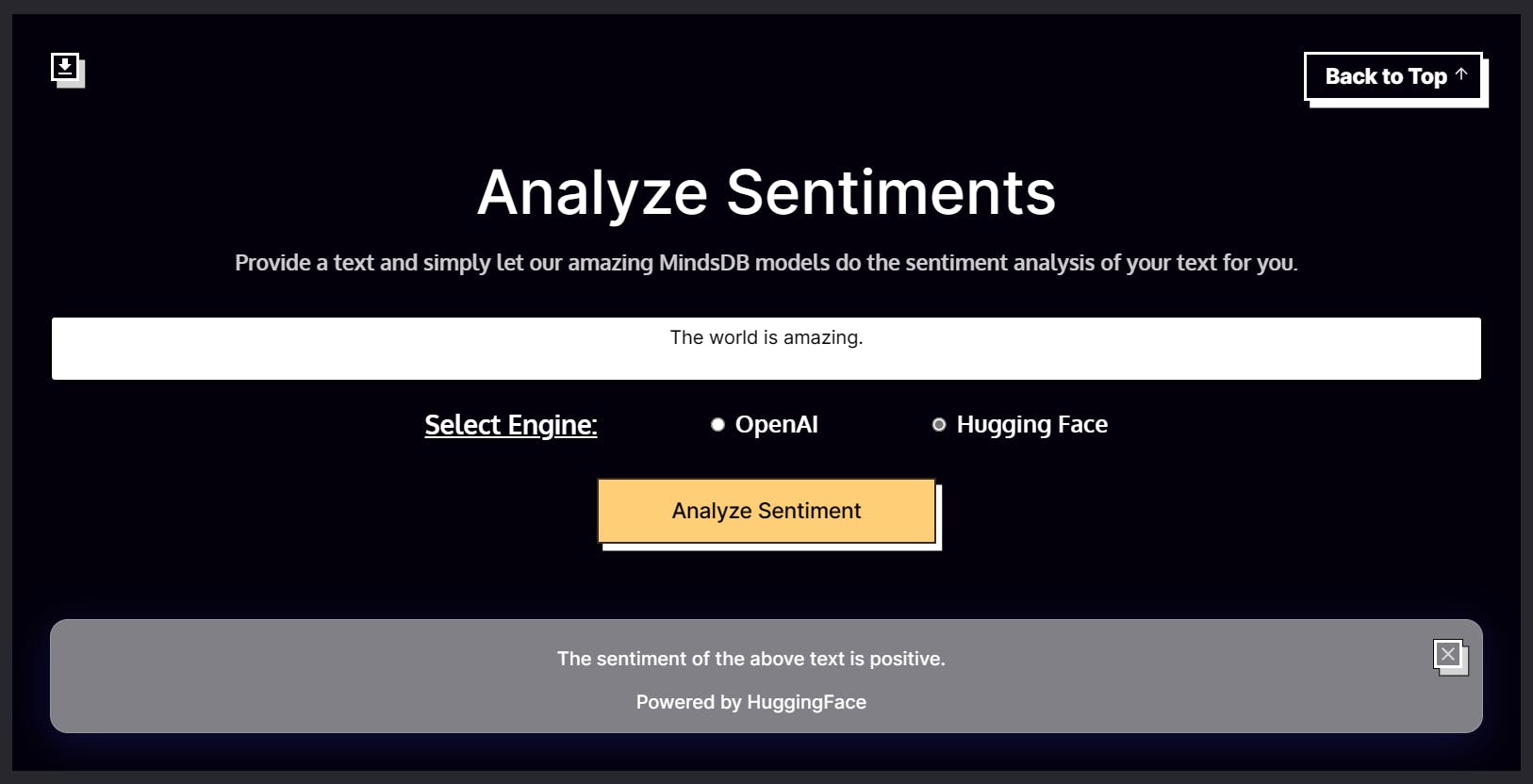
The 4 parameters for the Sentiment App will be as follows.
if (selectedEngine === "OpenAI") {
sentimentModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_SENTIMENT_MODEL_NAME;
} else if (selectedEngine === "HuggingFace") {
sentimentModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_SENTIMENT_MODEL_NAME;
}
const text = `SELECT sentiment FROM ${sentimentModelName} WHERE text="${inputText}"`;
const sentimentResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can provide the sentiment of the input texts.
For the OpenAI engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL openai_sentiment_analyzer
PREDICT sentiment
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
prompt_template = 'Describe the sentiment of the text
strictly as "positive", "neutral", or "negative".
"I love the product":positive
"It is a scam":negative
"{{text}}.":';
For the HuggingFace engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL hf_sentiment_analyzer
PREDICT sentiment
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'text-classification',
model_name = 'cardiffnlp/twitter-roberta-base-sentiment',
input_column = 'text',
labels = ['negative','neutral','positive'];
Translations
The Translations application allows users to translate text from one language to another. The app supports three translations, including English to French, French to English and Spanish to English. Users can input text in any of the supported languages, select the translation choice and the NLP engine of their choice (OpenAI or HuggingFace), and get back the translated text.
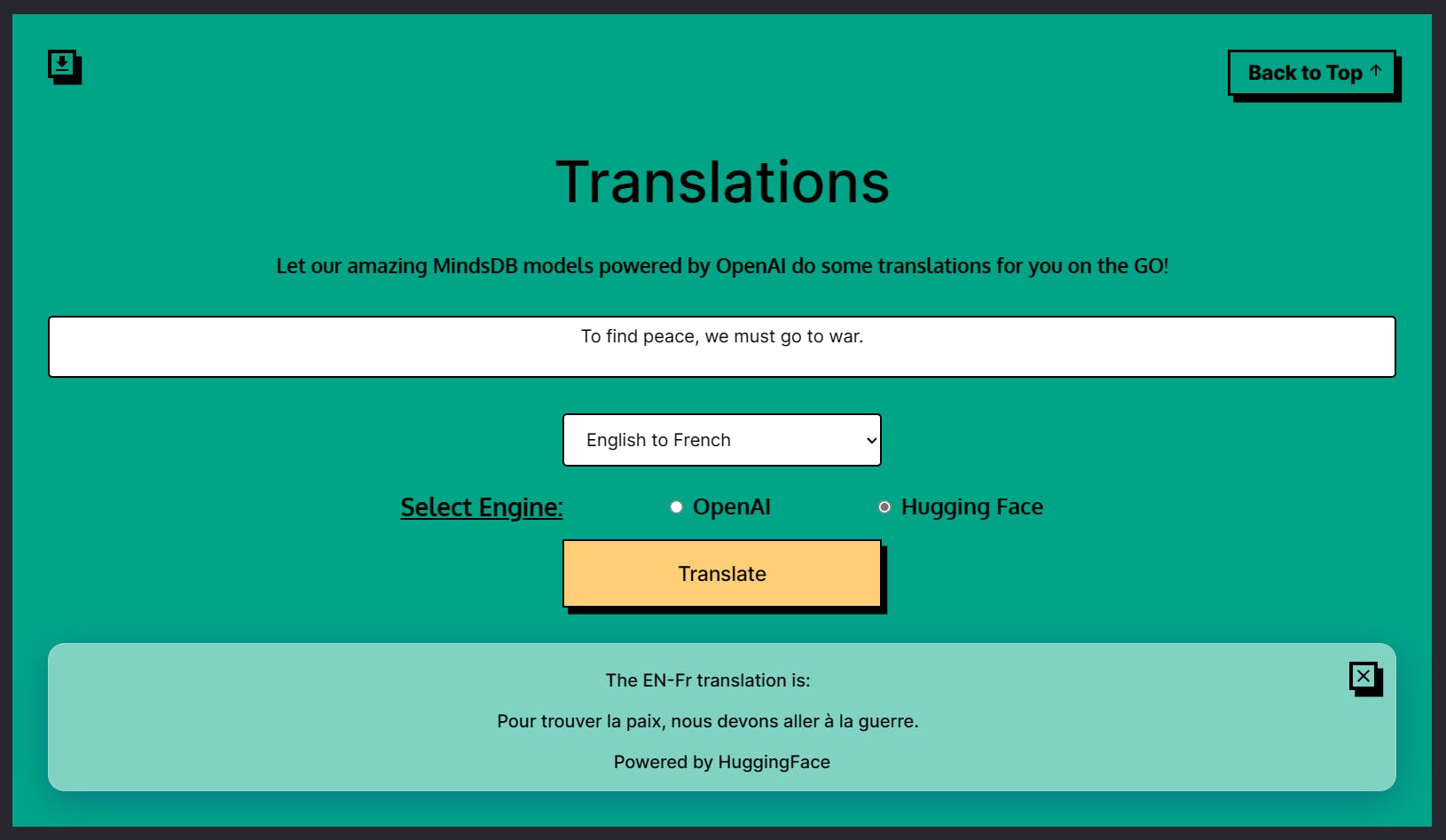
The 4 parameters will change as follows for the Translation App.
if (selectedEngine === "OpenAI") {
if (choice === "Fr-EN") {
translationModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_FREN_MODEL_NAME;
} else if (choice === "Es-EN") {
translationModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_ESEN_MODEL_NAME;
} else {
translationModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_ENFR_MODEL_NAME;
}
} else if (selectedEngine === "HuggingFace") {
if (choice === "Fr-EN") {
translationModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_FREN_MODEL_NAME;
} else if (choice === "Es-EN") {
translationModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_ESEN_MODEL_NAME;
} else {
translationModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_ENFR_MODEL_NAME;
}
}
const text = `SELECT translation FROM ${translationModelName} WHERE text="${inputText}"`;
const translationResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train 3 models using MindsDB Cloud that can translate the input texts.
For the OpenAI engine, we can create the models with the statements below.
CREATE MODEL openai_engfr_translator //English-French Model
PREDICT translation
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
prompt_template = 'Translate the following text in English to French. text:{{text}}';
-------------
CREATE MODEL openai_freng_translator //French-English Model
PREDICT translation
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
prompt_template = 'Translate the following text in French to English. text:{{text}}';
-------------
CREATE MODEL openai_speng_translator //Spanish-English Model
PREDICT translation
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
prompt_template = 'Translate the following text in Spanish to English. text:{{text}}';
For the HuggingFace engine, we can create the models with the statements below.
CREATE MODEL hf_enfr_translator //English-French Model
PREDICT translation
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'translation',
model_name = 't5-base',
input_column = 'text',
lang_input = 'en',
lang_output = 'fr';
-------------------
CREATE MODEL hf_fren_translator //French-English Model
PREDICT translation
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'translation',
model_name = 'Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-fr-en',
input_column = 'text',
lang_input = 'fr',
lang_output = 'en';
--------------------
CREATE MODEL hf_spen_translator //Spanish-English Model
PREDICT translation
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'translation',
model_name = 'Helsinki-NLP/opus-mt-es-en',
input_column = 'text',
lang_input = 'es',
lang_output = 'en';
Spam Detection
The spam detection app detects whether a given input text is spam. This app can help determine if an email or message is a scam. The app uses either the HuggingFace or the OpenAI engine based on the user's choice for spam detection.
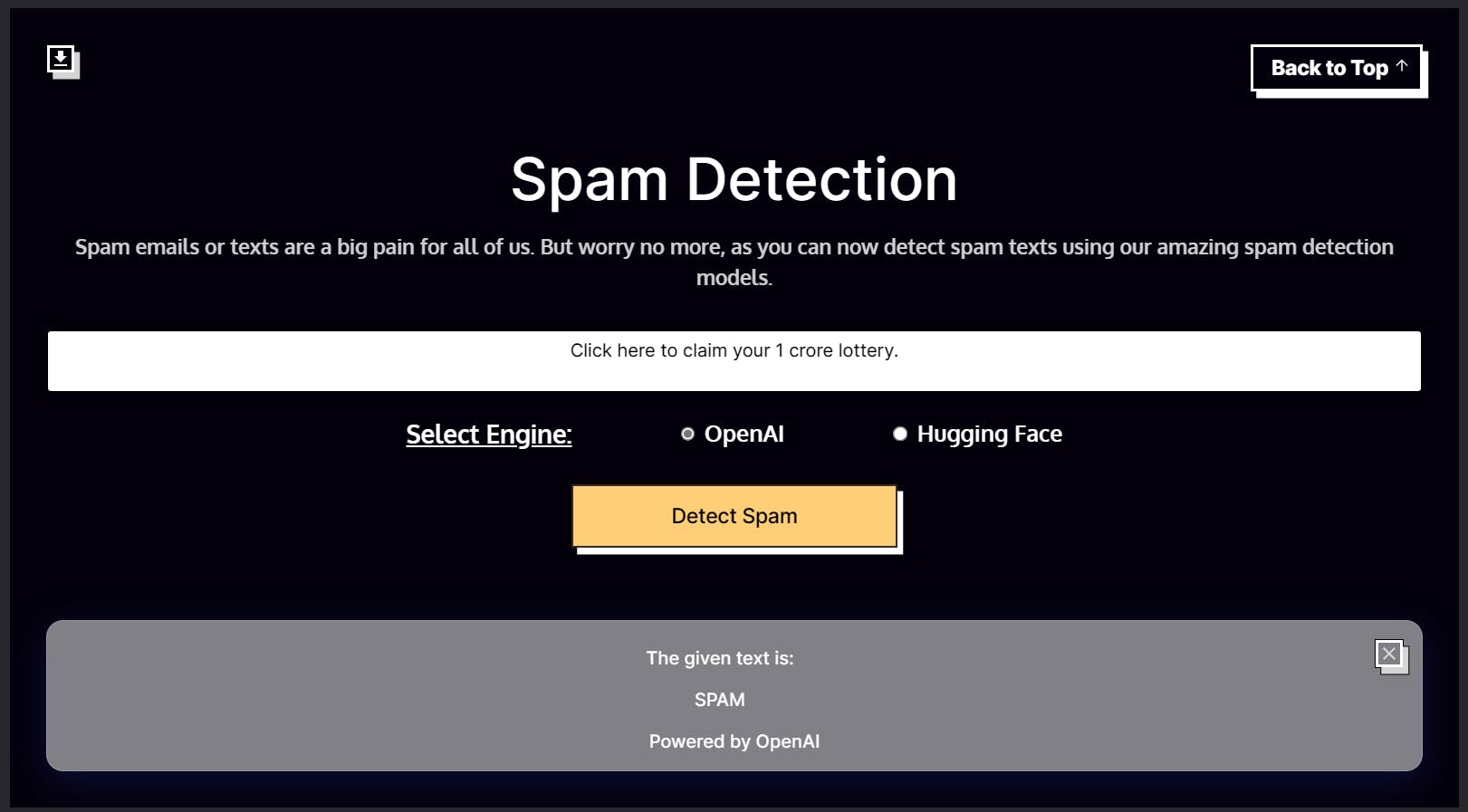
The 4 parameters for the Spam Detection App will be as follows.
if (selectedEngine === "OpenAI") {
spamModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_SPAM_MODEL_NAME;
} else if (selectedEngine === "HuggingFace") {
spamModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_SPAM_MODEL_NAME;
}
const text = `SELECT type FROM ${spamModelName} WHERE text="${message}"`;
const spamResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can detect spam from the input texts.
For the OpenAI engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL openai_spam_detector
PREDICT type
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
prompt_template = 'Determine and Label the given text as "SPAM" or "HAM".
"You have won 12 crore lottery. Click here to claim" : SPAM
"The team scrum call has been shifted to 8PM today. Kindly join on time." : HAM
"{{text}}" : ';
For the HuggingFace engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL mindsdb.hf_spam_detector
PREDICT type
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'text-classification',
model_name = 'mariagrandury/roberta-base-finetuned-sms-spam-detection',
input_column = 'text',
labels = ['HAM', 'SPAM'];
JSON Extraction
The JSON extraction app extracts JSON data in the defined format from a given input text. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. The app can be helpful for developers to extract meaningful data in the form of a JSON from a given string. The app uses the OpenAI engine for JSON extraction.
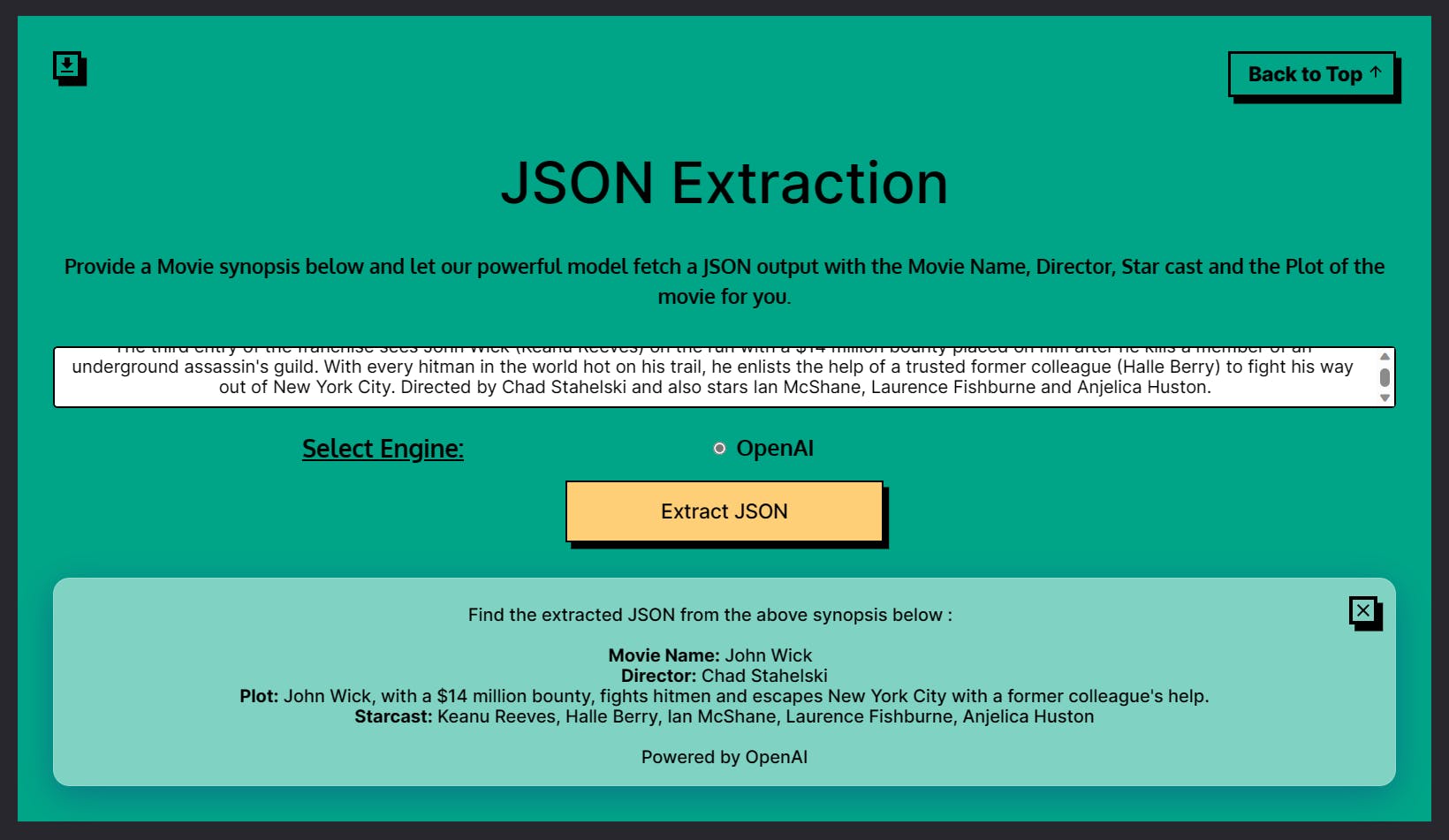
The 4 parameters for the JSON Extraction App are mentioned below.
if (selectedEngine === "OpenAI") {
jsonModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_JSON_MODEL_NAME;
}
const text = `SELECT json FROM ${jsonModelName} WHERE synopsis="${message}"`;
const jsonResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can extract data in a JSON format from the input texts.
For the OpenAI engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL openai_movie_json_extractor
PREDICT json
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
json_struct = {
'Movie': 'Movie Name',
'Director': 'Director',
'Starcast': 'Name of the stars or actors.',
'Plot': 'Short plot description about the movie in about 30 words.'
},
input_text = 'synopsis';
Question Answering
The question-answering app attempts to answer any question the user has based on the input text. The app uses the OpenAI engine for this. The model is trained such that it can answer questions without context.
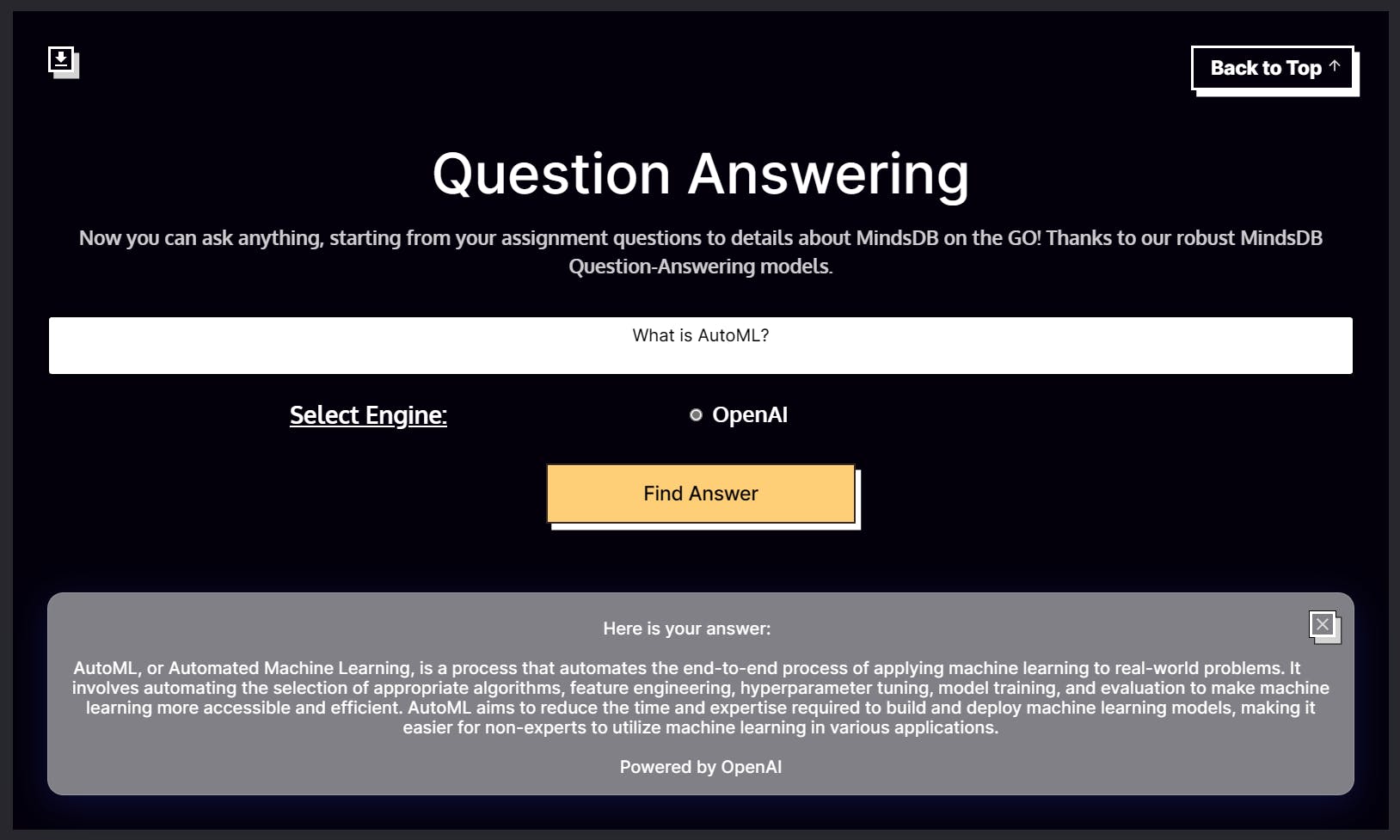
The 4 parameters for the Question Answering App will be as follows.
if (selectedEngine === "OpenAI") {
qnaModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_OA_QNA_MODEL_NAME;
}
const text = `SELECT answer FROM ${qnaModelName} WHERE question="${message}"`;
const qnaResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can answer the question in the input text.
For the OpenAI engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL openai_question_answerer
PREDICT answer
USING
engine = 'openai',
model_name = 'gpt-4',
prompt_template = 'Answer the following question. text:{{question}}.';
ESG Labelling
The ESG labelling app determines whether a given input text is environmentally, socially, or governance focused. ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance, and it is a set of standards used to measure the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment. This app can help determine if a company or an investment is ESG focused. The app uses the HuggingFace engine for ESG labelling.
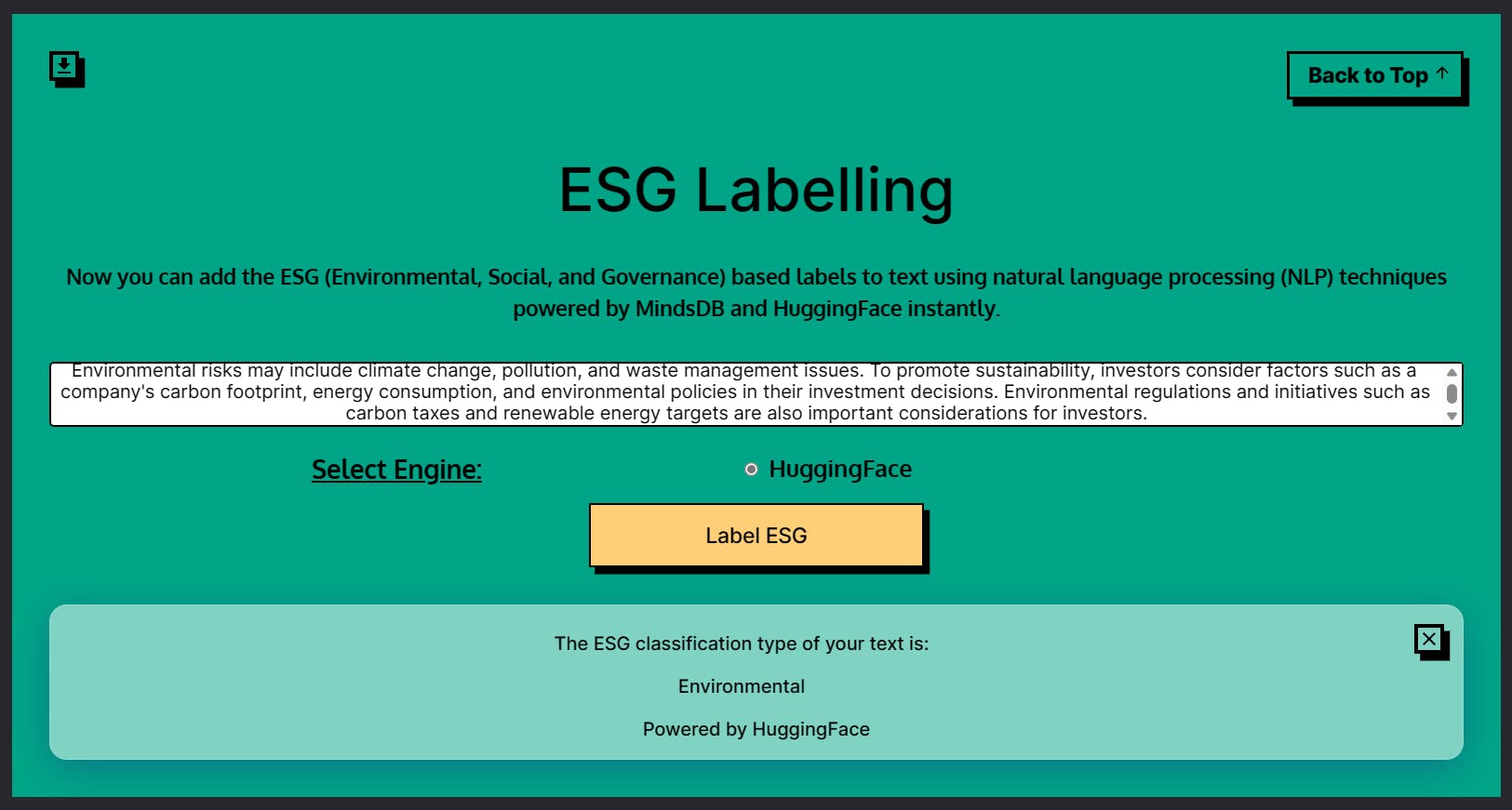
The 4 parameters for the ESG Labelling App will be as follows.
if (selectedEngine === "HuggingFace") {
esgModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_ESG_MODEL_NAME;
}
const text = `SELECT label FROM ${esgModelName} WHERE text="${message}"`;
const esgResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can label ESG types properly based on the input texts.
For the HuggingFace engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL mindsdb.hf_esg26_labeller
PREDICT label
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'text-classification',
model_name = 'yiyanghkust/finbert-esg',
input_column = 'text';
Industry Identification
The industry identification app attempts to identify the industry a company belongs to based on the input text. This app can be helpful for investors to know which industry a company belongs to. The app uses the HuggingFace engine for industry identification.
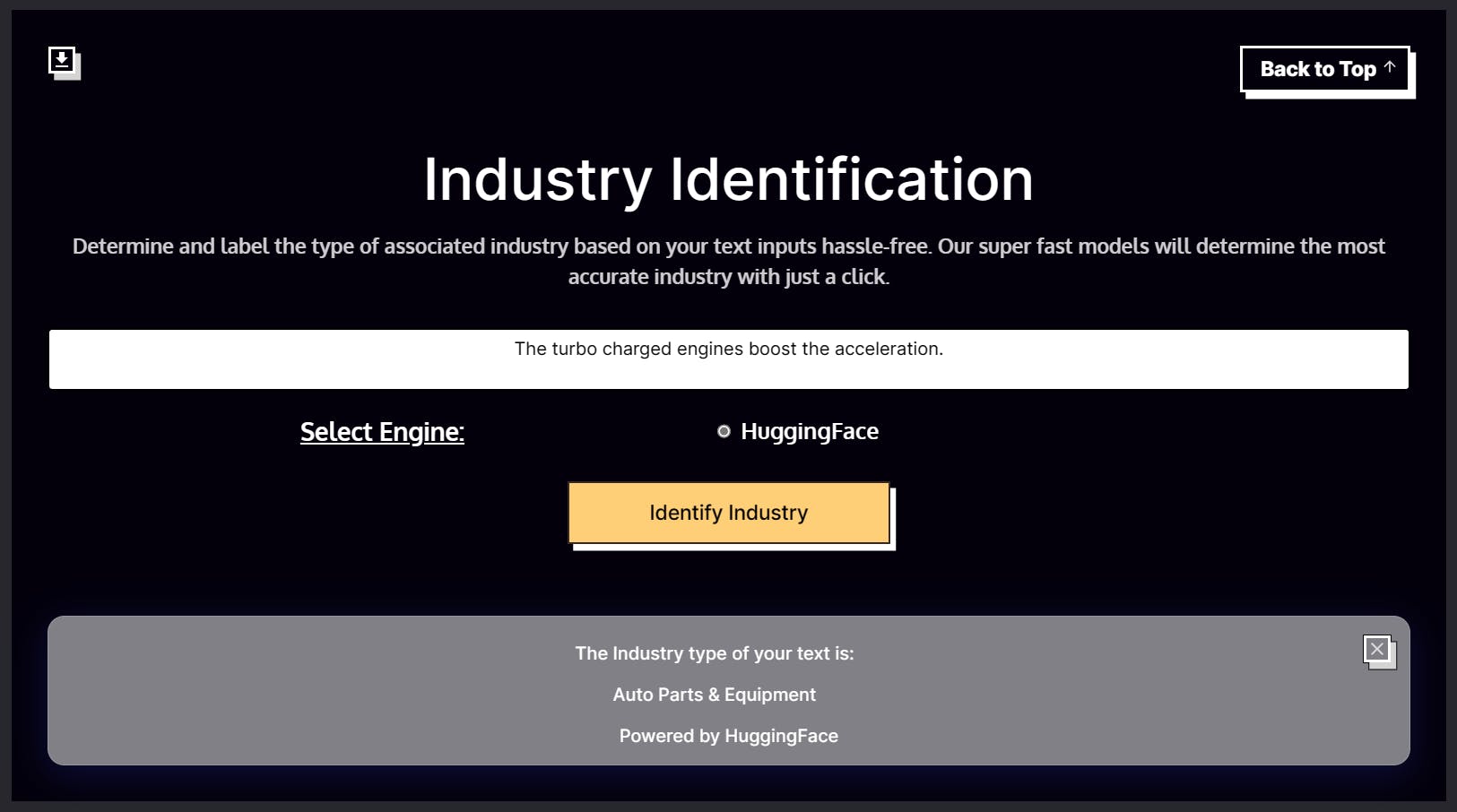
The 4 parameters for the Industry Identification App are as follows.
if (selectedEngine === "HuggingFace") {
industryModelName = process.env.MINDSDB_HF_INDUSTRY_MODEL_NAME;
}
const text = `SELECT label FROM ${industryModelName} WHERE text="${message}"`;
const industryResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can identify the respective industry from the input texts.
For the HuggingFace engine, we can create a model with the statement below.
CREATE MODEL mindsdb.hf_industry_labeller
PREDICT label
USING
engine = 'huggingface',
task = 'text-classification',
model_name = 'sampathkethineedi/industry-classification',
input_column = 'text';
Prediction Models
MindsDB also offers to train robust predictor models that can be used to predict an outcome. These models can be prepared using existing data in the database and don't necessarily need any coding skills or expertise in programming. The models here work in a similar way as the above NLP models but with a slight change. They don't require any modelName or selectedEngine parameters.
Mobile Price Prediction
The mobile price prediction app predicts the price of a mobile device based on its input features such as RAM, battery, etc. The app uses MindsDB's regression predictor model to predict accurate pricing.

The 2 parameters for the Mobile Prediction app are as follows.
const text = `Select Price from ${priceModelName} where Brand="${request.body.brand}" AND Model="${request.body.model}" AND Storage=${request.body.storage} AND RAM=${request.body.ram} AND ScreenSize=${request.body.screen} AND BatteryCapacity=${request.body.battery} AND Camera=${request.body.camera};`;
const priceResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can predict the price of a phone based on user-provided input specs.
We can create a regression predictor model for this with the statement below.
Create Predictor mindsdb.mobile_price_predictor
FROM files
(Select * from Mobiles)
Predict Price;
Ethereum Price Prediction
The Ethereum Price Prediction app predicts the future price of Ethereum, a cryptocurrency. The app uses MindsDB's time-series predictor model to forecast the price of Ethereum on the next day of the user-provided date.
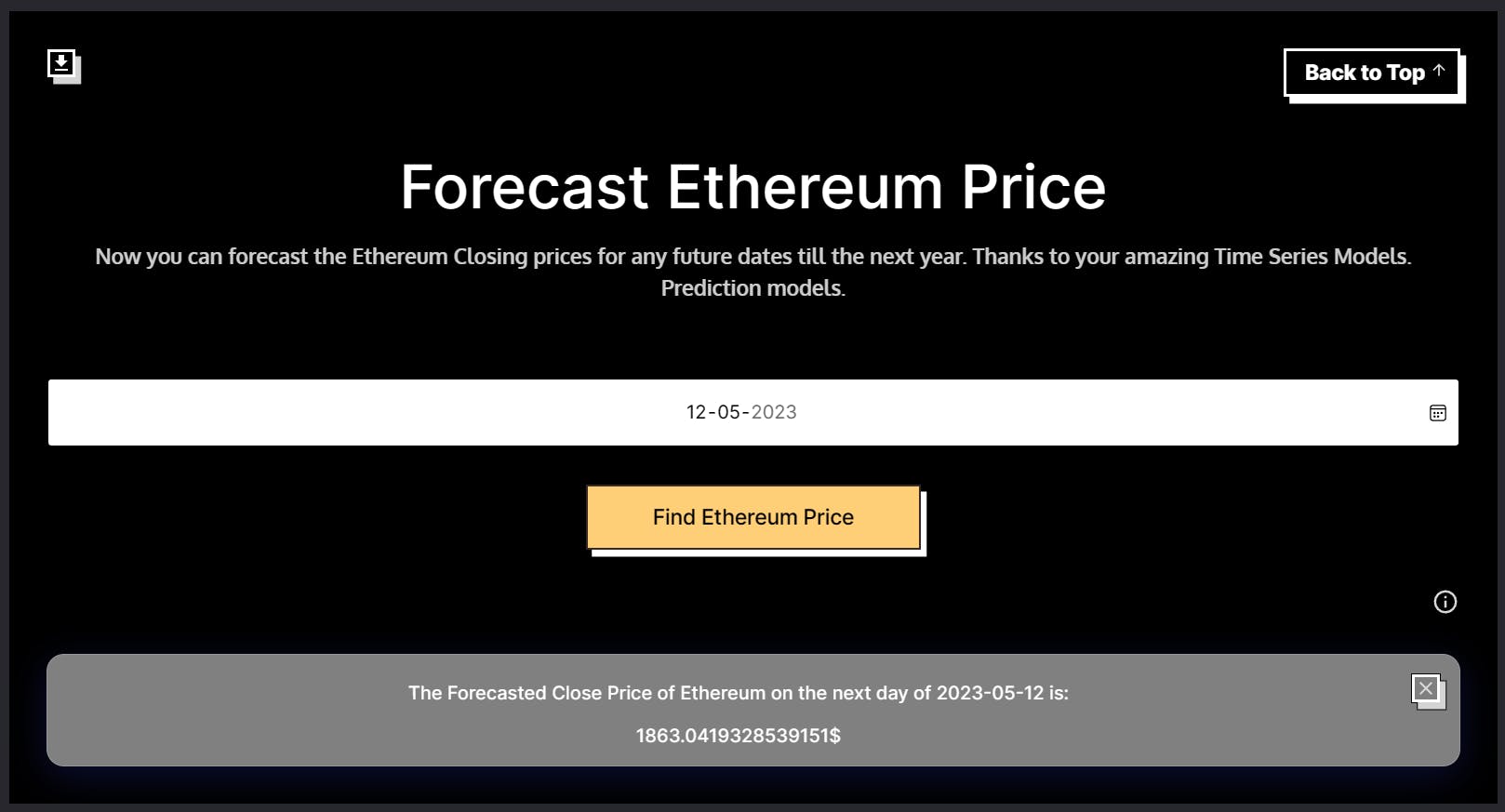
The 2 parameters for the Ethereum Price Prediction App will be as follows.
const text = `Select EP.Close from ${ethModelName} as EP JOIN files.Ethereum as E WHERE E.Date > '${request.body.date}' LIMIT 1;`;
const ethPriceResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can forecast the Ethereum price for the next day of the date given by the user.
We can create a time-series model for this with the statement below.
CREATE PREDICTOR mindsdb.ethereum_price_predictor
FROM files
(Select * from Ethereum)
PREDICT Close
ORDER BY Date
WINDOW 150
HORIZON 65;
Water Potability Prediction
The water potability prediction app predicts whether a given water sample is safe for human consumption or not. The app uses MindsDB's classification predictor model to determine water portability based on the user's water composition parameters.
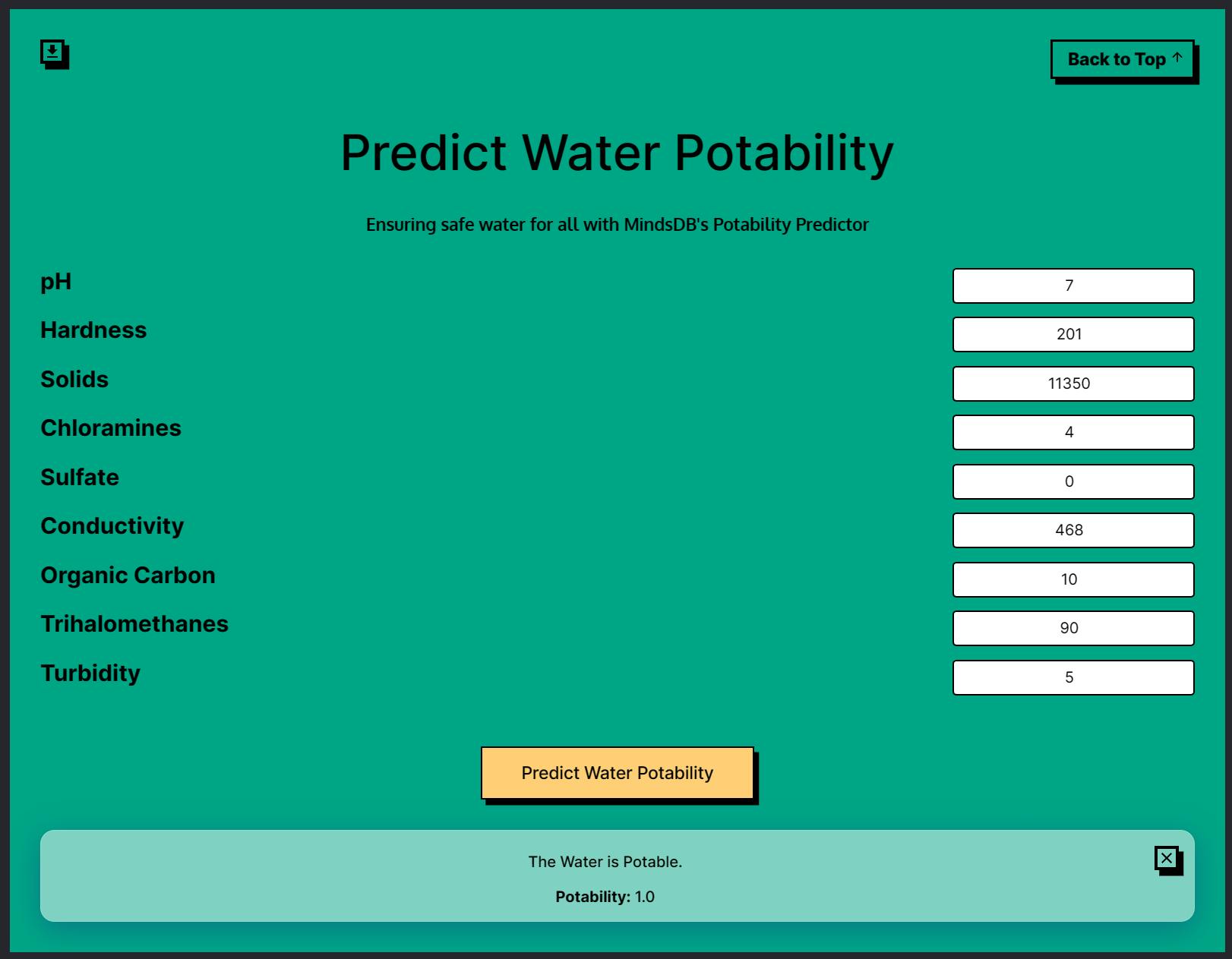
The 2 parameters for the Water Potability App will be as follows.
const text = `Select Potability from ${waterModelName} where ph=${request.body.ph} AND Hardness=${request.body.hardness} AND Solids=${request.body.solids} AND Chloramines=${request.body.chloramines} AND Sulfate=${request.body.sulfate} AND Conductivity=${request.body.conductivity} AND Organic_carbon=${request.body.carbon} AND Trihalomethanes=${request.body.trihalomethanes} AND Turbidity=${request.body.turbidity};`;
const waterResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can classify the water potability based on the water composition from the input texts.
We can create a classification model for this with the statement below.
CREATE PREDICTOR mindsdb.water_potability_predictor
FROM files
(SELECT * FROM Water)
PREDICT Potability;
Tesla Stock Price Prediction
The Tesla stock price prediction app predicts the future price of Tesla's stock. The app again uses MindsDB's time-series predictor model to forecast the stock price of Tesla on the next day of the user-given date.
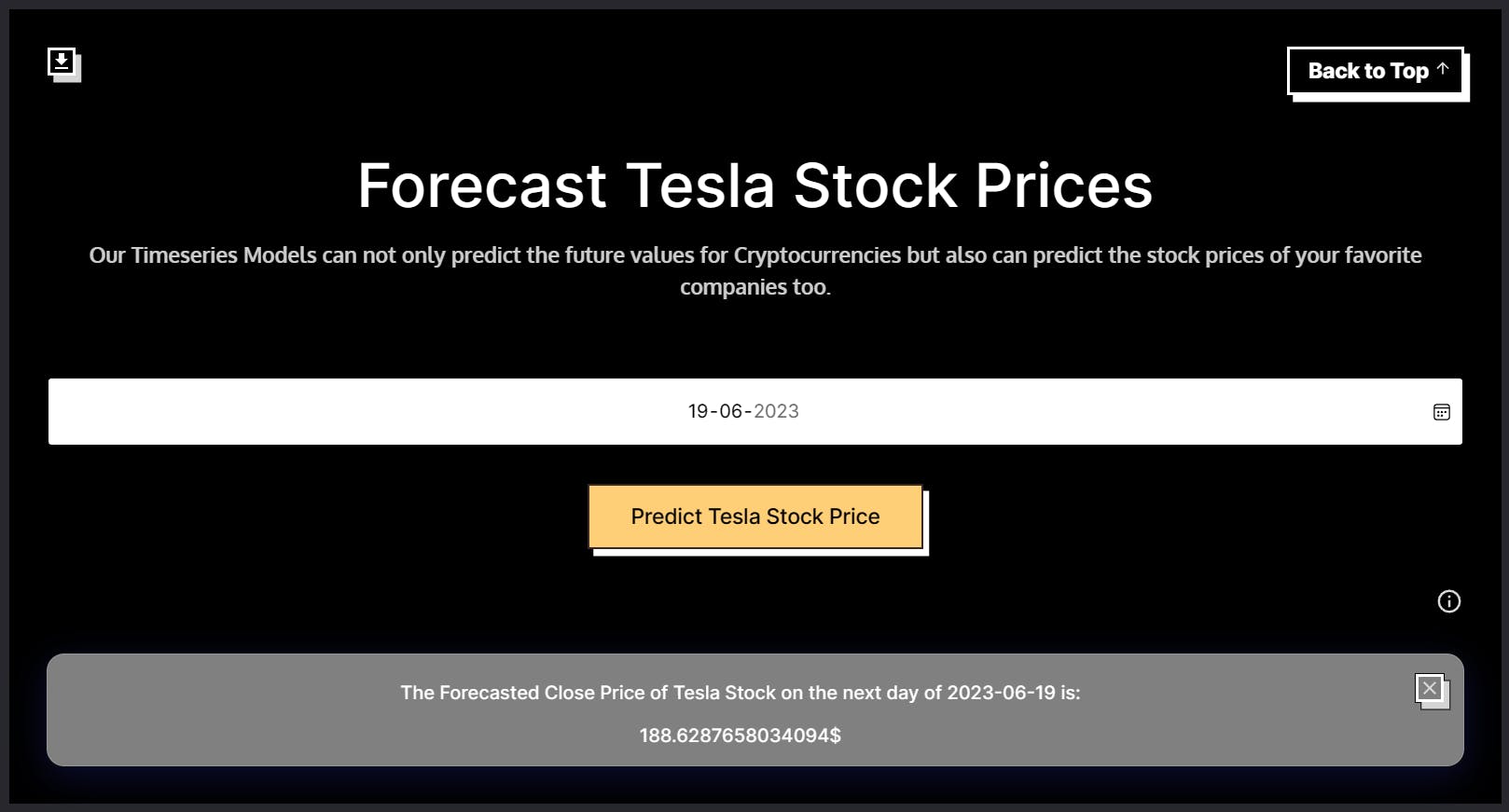
The 2 parameters for the Tesla Stock Prediction App will be as follows.
const text = `Select TP.Close from ${teslaModelName} as TP JOIN files.Tesla as T WHERE T.Date > '${req.body.date}' LIMIT 1;`;
const priceResponse = await MindsDB.SQL.runQuery(text);
Now, we need to train a model using MindsDB Cloud that can forecast the Tesla Stock price for the next day of the date given by the user.
We can create a time-series model for this with the statement below.
CREATE PREDICTOR mindsdb.tesla_stocks_predictor
FROM files
(Select * from Tesla)
PREDICT Close
ORDER BY Date
WINDOW 150
HORIZON 65;
App Features
The MindsDB Playground App has several features that make it a useful tool for users of all levels to get started with MindsDB. Some of these salient features include:
Easy-to-use Interface: The app comes with a user-friendly interface that makes it easy for users to interact with a variety of apps powered by MindsDB.
Free-to-use: The app is free to use and will always stay that way.
Various NLP Models: The app has eight NLP applications powered by the OpenAI engine or the HuggingFace engine. These applications include Text Summarization, Sentiment Analysis, Translations (Eng-Fr, Fr-Eng, Es-Eng), Spam Detection, JSON Extraction, Question Answering, ESG Labelling, and Industry Identification.
Various Prediction Models: The app also offers four prediction applications, including Mobile Price Prediction, Ethereum Price Prediction, Water Potability Prediction, and Tesla Stock Price Prediction. These 4 apps cover all the different types of prediction models i.e., Regression Type, Classification Type and Timeseries Type.
Mobile Responsive: The Playground application is designed to be easily usable on various types of devices including, mobile phones (both in portrait and landscape modes), tablets, laptops and desktops.
SQL Cheat Sheets: In case any new user wonders how to train the models that are present on the Playground application themselves on MindsDB Cloud, they can simply use the
Download Cheat Sheetoption present at the top left corner of each of the application panels.Cloud Hosting: The Playground App has been deployed live using the DigitalOcean App Platform which is very reliable and fail-safe.
Custom Domain: The Playground App uses a custom domain to add a sense of branding and credibility among its users and is also secured with SSL i.e. you can access it over HTTPS.
Demo
The app has been deployed and is live on MindsDB Playground.
The GitHub repository for the project can be found here.
Future Scopes
The Playground App is currently under early development and the recent release can be considered as a version 1 release. So, like any other app, it has many scopes of improvement. However, some of the major ones are listed out below.
More Sample Apps
Faster Response Times
Session Cache
Sample Dataset Downloads
Modern UI Framework Implementation
Conclusion
Overall, the MindsDB Playground App provides an excellent opportunity to explore the capabilities of natural language processing and predictive analytics that are powered by MindsDB. The app's user interface is user-friendly, and the app is easy to use. Users can choose between different NLP and predictive analytics models and select the one that they want to use. The app can be useful for new users, potential customers, developers and anyone interested in exploring the robust and accurate solutions provided by MindsDB.
Lastly, feel free to drop any suggestion or feedback about the App in the comments below and don't forget to show some appreciation to this article if you had a great time reading it.
References